A recent Bloomberg article, (Misfiring Models Leave Wall Street Currency Traders Flying Blind) raised some important questions about the challenges facing currency markets today. Here, we pick up where the article left off, examining the forces behind the dollar’s recent moves and addressing the gaps in conventional theories.
It’s not about carry. U.S. interest rates are down year to date, but so are the rates of most other major global currencies (except for the yen). In fact, U.S. rates have declined by only a little less than the average interest rate drop among the G10.
Average Change in Two-Year Swap Rates: U.S. vs. G10
31 Dec 2024 - 8 Jul 2025 (Pct Points)
Could it be purchasing power parity (PPP) making a comeback? The dollar has long been overpriced based on most models. But overvaluation alone doesn’t typically explain such a sharp dollar downturn. It’s also strange that the yen, which is the most undervalued against its PPP level (-36%), has appreciated the least. And what about the Swiss franc? It’s now 20% overvalued on a PPP basis yet has climbed roughly 13% against the dollar this year, making it the second-best performer.
Does the answer lie in tariff turmoil? Before April’s “Liberation Day,” tariffs were broadly expected to strengthen the dollar. The logic was simple: U.S. trading partners would depreciate their currencies to offset the higher costs of exporting to the U.S. Yet the dollar remains below its pre-Liberation Day levels, unlike the rebound seen across most other U.S. assets.
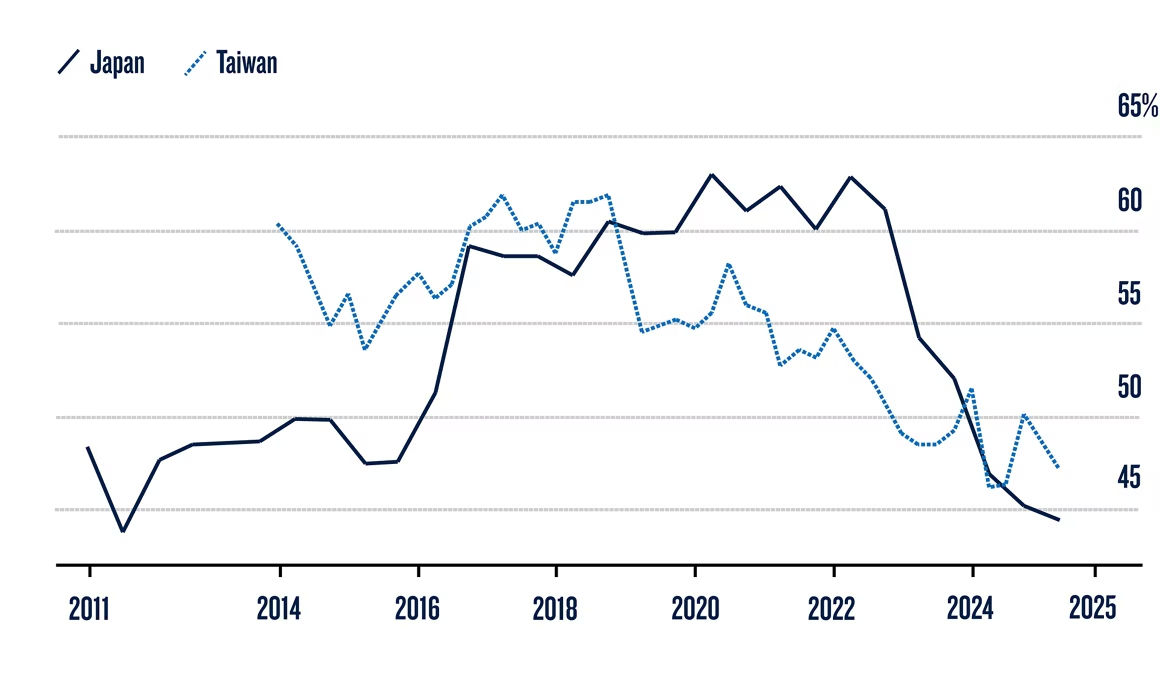
One intriguing possibility gaining attention is hedging. The theory here is that non-U.S. investors have to remain invested in U.S. assets, but are reducing exposure to U.S. currency risk by selling dollars. And while this might contribute in part to the dollar’s decline, it doesn’t seem sufficient to explain its scale or breadth. For instance, Japanese life insurers, which are among the largest private holders of U.S. assets, have reduced their hedge ratios to multi-year lows1. Meanwhile, Taiwan life insurers have seen a slight uptick in hedging activity, though their levels remain low2. For both, hedging is quite costly, because it is expensive to sell dollars when U.S. short-term interest rates outpace local rates.
Life Insurers Cut FX Hedging Both in Taiwan and Japan
Ratios of Foreign Exchange Derivatives to Overseas Assets
Source: Bloomberg - Taiwan Life Insurers Caught in Dilemma With Costly FX Hedges
And so it goes. While every theory has its gaps, there are some things that have worked:
First, some core “macro” inputs like growth forecasts and economic data surprises. These have had a good record so far this year for gauging the dollar’s moves. A currency, in some sense, is the sum total of the value of its economy, so macro data should be a primary driver of currencies.
Second, measures that quickly capture shifts in the risk environment. Risk sentiment has fluctuated sharply, particularly after the April 9 “pause” in reciprocal tariffs. Since then, positive trade news has repeatedly eased risk aversion, pulling the dollar lower.
This trend has become more pronounced in recent years. “Risk-off” events in currency markets have tended to be quite short, quickly swinging back to “risk-on” conditions. The days when investors could rely on holding the dollar, Swiss franc, and Japanese yen for months during bouts of risk aversion seem to be over. Or more precisely, the specific risk scenarios that favour these currencies have become increasingly rare. Instead, risk-off events are driven more by liquidity concerns and are often mitigated by policy intervention.
If “macro” and “risk” factors are performing well, that’s a pretty good sign. Currencies are never driven by just one factor, like carry. Relying on such models alone invites what the Bloomberg article aptly calls “misfires.” Successful strategies incorporate multiple factors to compensate when the usual triggers, like carry, falter.
Source: PGIM Quantitative Solutions as of July 2025. Forecasts may not be achieved and are not a guarantee or reliable indicator of future results.
References to specific securities and their issuers are for illustrative purposes only and are not intended and should not be interpreted as recommendations to purchase or sell such securities. The securities referenced may or may not be held in the portfolio at the time of publication and, if such securities are held, no representation is being made that such securities will continue to be held.
The views expressed herein are those of PGIM investment professionals at the time the comments were made, may not be reflective of their current opinions, and are subject to change without notice. Neither the information contained herein nor any opinion expressed shall be construed to constitute investment advice or an offer to sell or a solicitation to buy any securities mentioned herein. Neither PFI, its affiliates, nor their licensed sales professionals render tax or legal advice. Clients should consult with their attorney, accountant, and/or tax professional for advice concerning their particular situation. Certain information in this commentary has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable as of the date presented; however, we cannot guarantee the accuracy of such information, assure its completeness, or warrant such information will not be changed. The information contained herein is current as of the date of issuance (or such earlier date as referenced herein) and is subject to change without notice. The manager has no obligation to update any or all such information; nor do we make any express or implied warranties or representations as to the completeness or accuracy.
Any projections or forecasts presented herein are subject to change without notice. Actual data will vary and may not be reflected here. Projections and forecasts are subject to high levels of uncertainty. Accordingly, any projections or forecasts should be viewed as merely representative of a broad range of possible outcomes. Projections or forecasts are estimated based on assumptions, subject to significant revision, and may change materially as economic and market conditions change.
4665301